
11. ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS – LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
11. ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
Q. 1. Explain giving reasons :
(i) Boiling point of an alcohol is higher than the corresponding alkane.
(ii) Lower alcohols are soluble in water, while the higher alcohols are not.
(iii) Boiling point of mono hydric alcohols increases with increase in carbon atoms.
Ans⇒ (i) The boiling points of alcohols are higher than those of the corresponding alkanes, due to the intermolecular association of a large number of alcohol molecules through hydrogen bonding. Thus
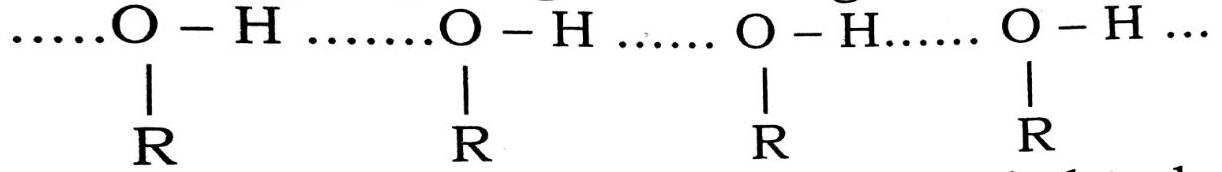
Since a large amount of energy is needed to break the extensive hydrogen bonds, which hold a lage number of alcohol molecules together, so the boiling points of alcohols are significantly higher than the corresponding alkanes, in which no such hydrogen bonding can taken place.
(ii) The solubility of an alcohol in water depends upon its capacity to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, the non-polar hydrocarbon part of the alcohol molecule is unable to form hydrogen bonds with other. Consequently, the lower alcohols are soluble in water, due to the formation of hydrogen bonds between highly polarise hydroxyl group (-OH), present in alcohols as well as water. However, in higher alcohols the hydrocarbon part becomes larger in size and, therfore, the solubility effect due to hydroxyl groups (-OH), of alcohol is out weighed by the counter large ‘repulsive effect’ of non-polar hydrocarbon part of the alcohol molecule. Hence, higher alcohols become in soluble in water. The large inductive effect (+ I effect) of the hydrocarbon part (or alkyl group) in higher alcohols also reduces the polar character of hydroxyl group ( OH) in higher alcohols, which in turn reduces their capacity to form hydrogen bonding with water.
(iii) With the increase in molar mass of alcohol, the intermolecular Van der Waals forces of attraction increases, thereby the boiling point also increases. Thus b.p. of
C4H5OH > C3H7OH > C2H5OH > CH3OH
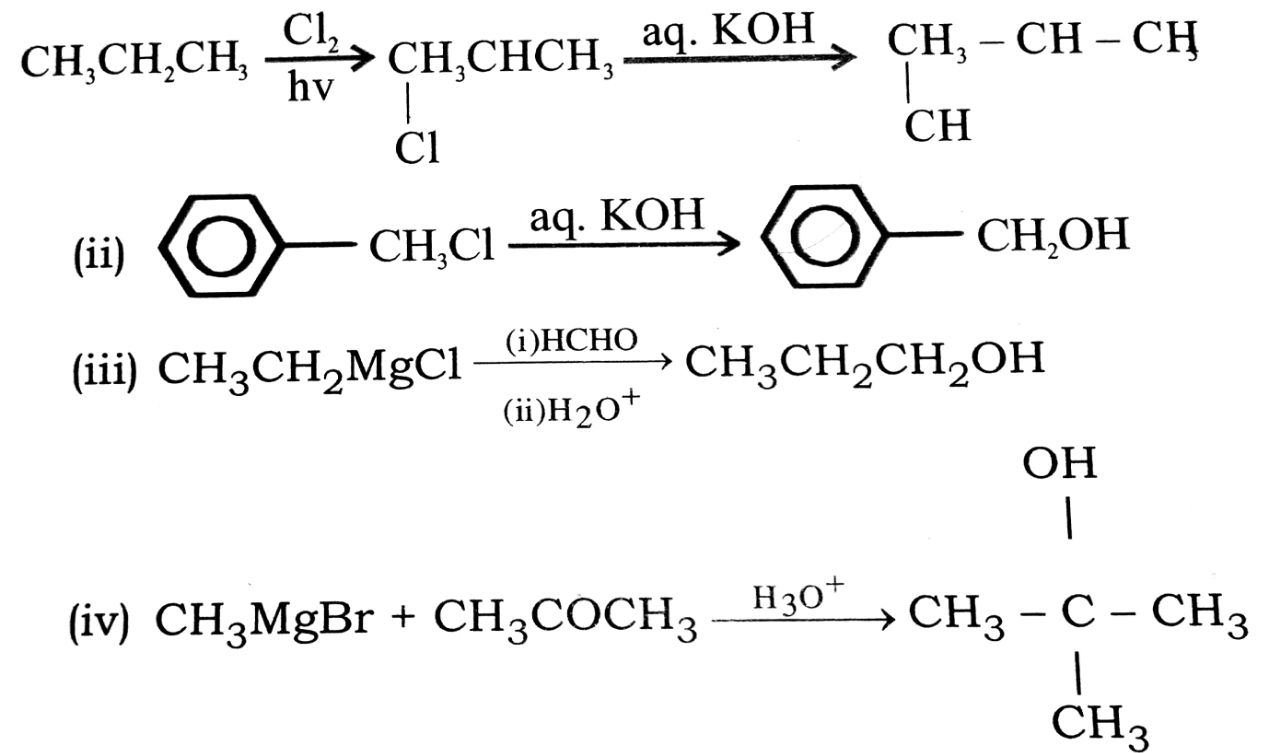
Q. 2. How are the following conversions carried out ?
(i) Propane → Propane-2-ol.
(ii) Benzyl chloride → Benzyl alcohol.
(iii) Ethyl magnesium chloride → Propane-1-ol.
(iv) Methyl magnesium bromide → 2-methy14) propan-2-ol.
Ans⇒ (i)
Q. 3. Given the structure and IUPAC name of the expected product of the follwoing reactions :
(i) Catalytical reduction of butanal.
(ii) Hydroboration of but-1-ene.
(iii) Hydration of propylene in presence of dil. sulphuric acid.
(iv) Reaction of propanone with ethyl magnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis of the product.
Ans⇒ (i) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH Butan-1-ol
(ii) CH2CH2CH2CH2OH Butan-1-ol

Q. 4. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds :


Ans⇒ (i) 2, 2, 4-Trimethyl pentan-3-ol.
(ii) 5-Ethyl heptane-2, 4-diol
(iii) Butane-2, 3-diol.
(iv) Propane-1, 2, 3-triol.
(v) 2-Methyl phenol.
(vi) 4-Methyl phenol.
(vii) 2, 5-Dimethyl phenol.
(viii) 2, 6-Dimethyl phenol.
(ix) 1-Methoxy-2-methyl propane.
(x) Ethoxy benzene.
(xi) 1-Phenoxy heptane.
(xii) 2-Ethoxy butane.
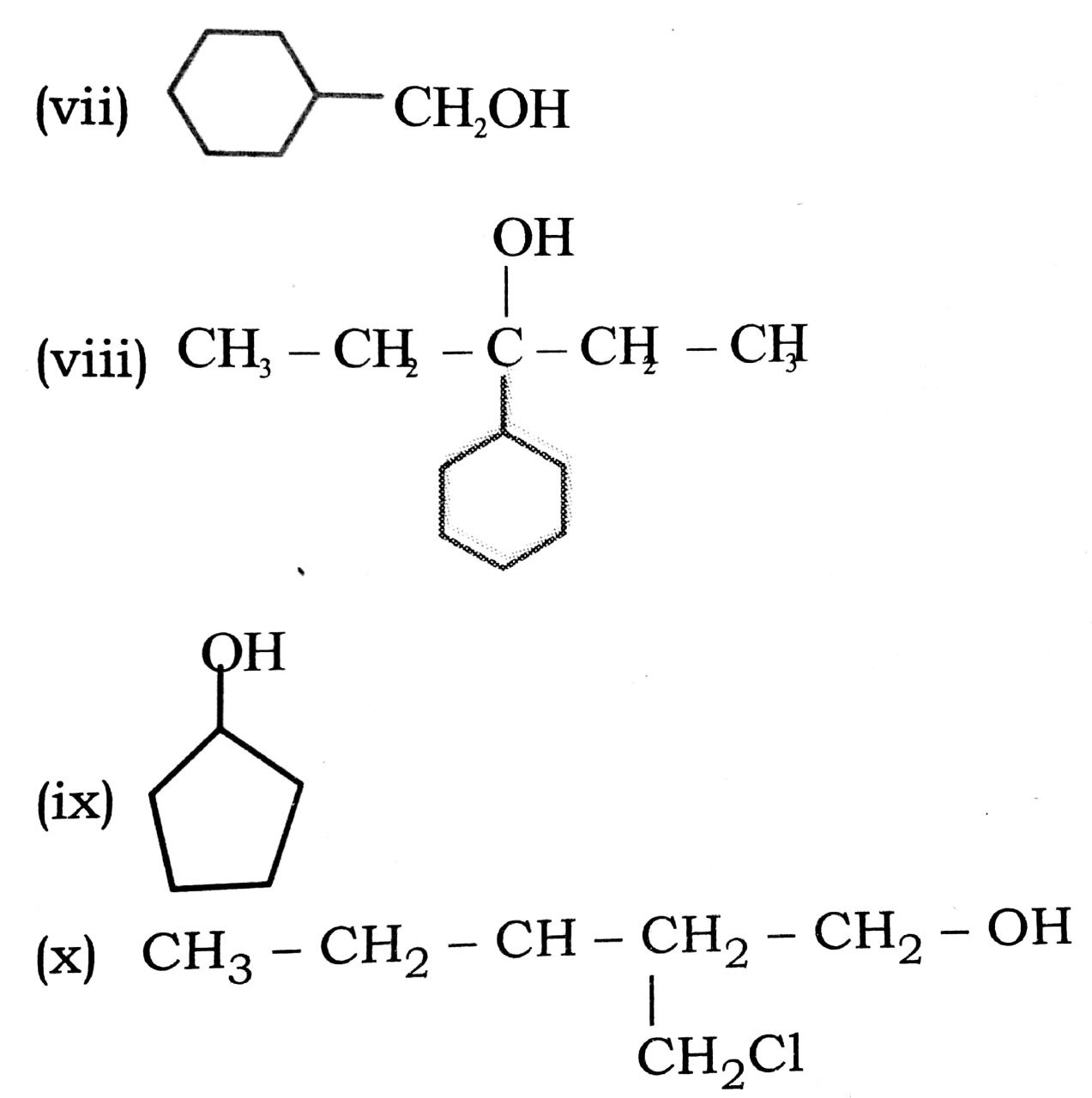
Q. 5. Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows :
(i) 2-Methyl butan-2-ol.
(ii) 1-Phenyl propan-2-ol.
(iii) 3, 5-Dimethyl hexane-1, 3, 5 triol.
(iv) 2, 3-Diethyl phenol.
(v) 1-Ethoxypropane.
(vi) 2-Ethoxy-3-methyl pantane.
(vii) Cyclo hexyl ethanol.
(viii) 3-Cyclo hexyl pentan-3-ol.
(ix) cyclopent-3-en-1-ol.
(x) 3-Chloro methyl pentan-1-01.

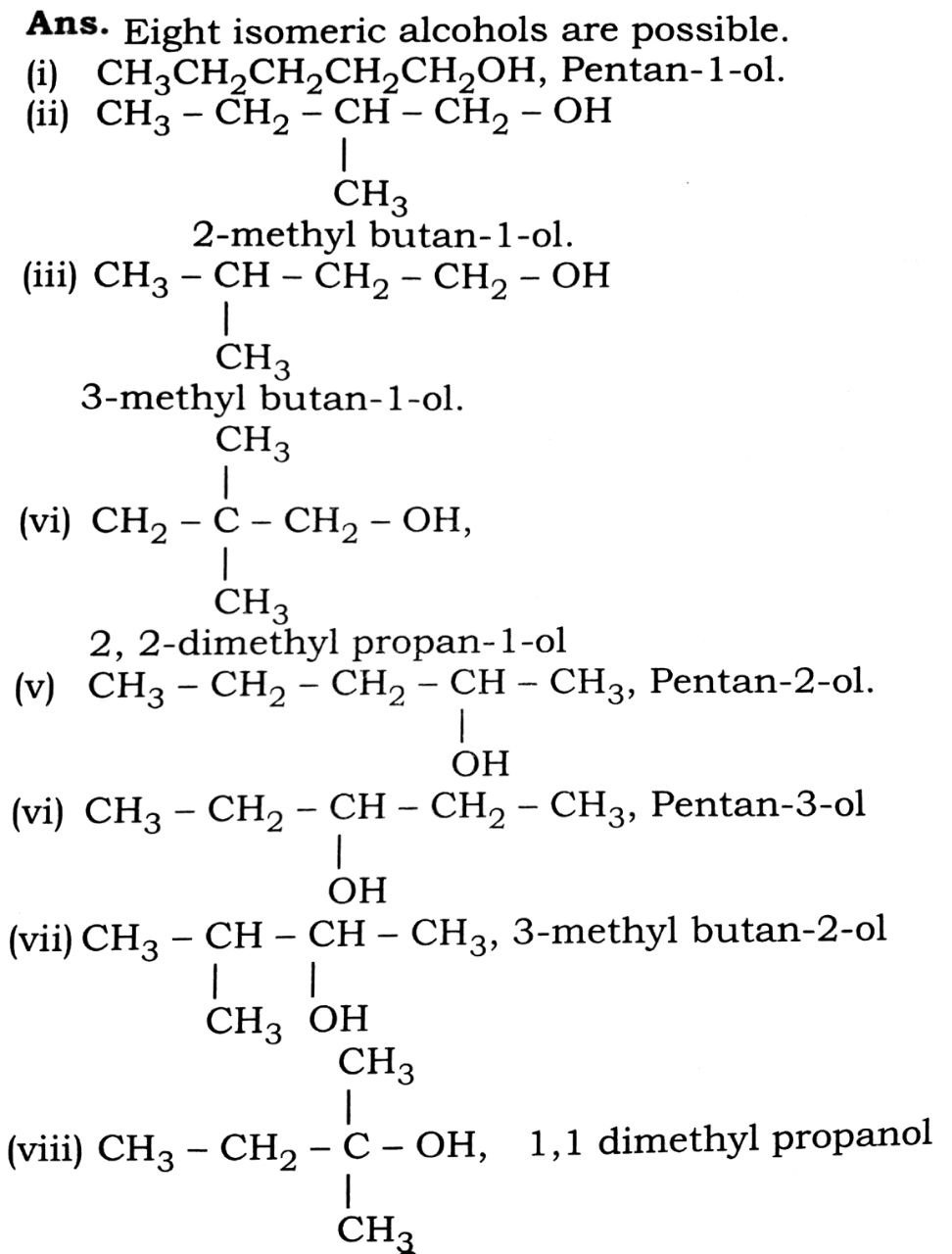
Q. 6. Draw the structure of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C3H120 and give their IUPAC names.
Ans⇒ Eight isomeric alcohols are possible.
(i) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH, Pentan-1-ol.
Q. 7. Give two reåctions that show the acidic nature of phenol. Compare acidity of phenol with that of ethanol.
Ans⇒ (i) Reaction with active metals : Phenol reacts with active metals like Na, K, etc. and H2 is evolved.
 (ii) Reaction with alkalies : Phenol neutralises the caustic alkalies such as NaOH or KOH to form salt and water.
(ii) Reaction with alkalies : Phenol neutralises the caustic alkalies such as NaOH or KOH to form salt and water.

Phenol shows a considerable acidic character as compared to that of ethanol. It is because of structural difference in C6H5 and C2H5 parts of the two molecules.
CH3 →- CH2 →- O →-H
(i)
Oxygen connected to sp3 hybridized C atom which is less electronegative and has electron repelling nature. This makes- O – H bond less polar and release of H becomes more difficult. Alkoxide ion formed is not stabilized by resonance. 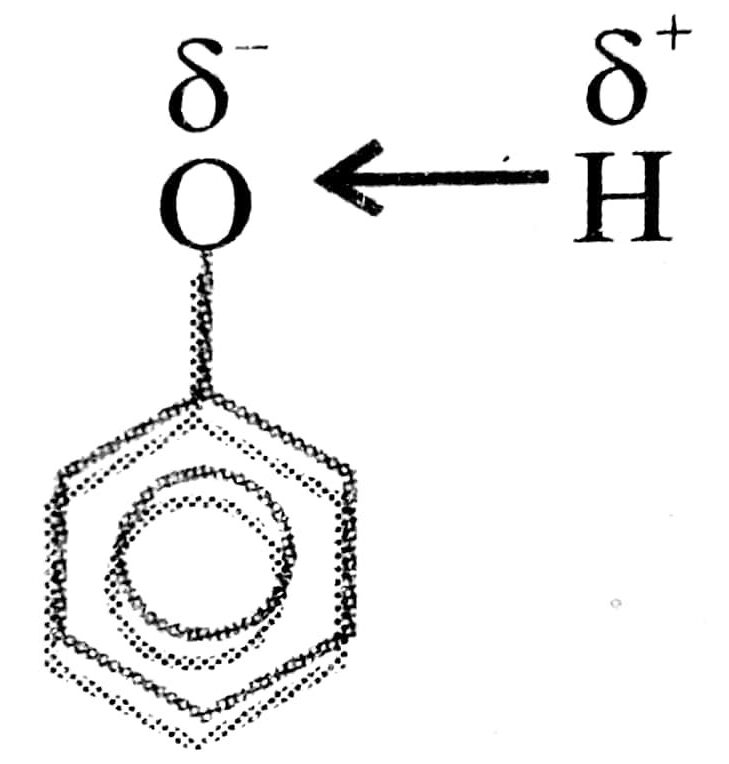
(ii)
Oxygen atom connected to sp2 hybridized C atom of benzene ring which is more electro negative than sp3 hybridized carbon atom. This makes 0-H bound more polar and His released easily. Penoxide ion formed is stabilised by resonance.
Q. 8. Give TUPAC names of the following ethers :
(i) C2H5OCH3 – CH – CH3

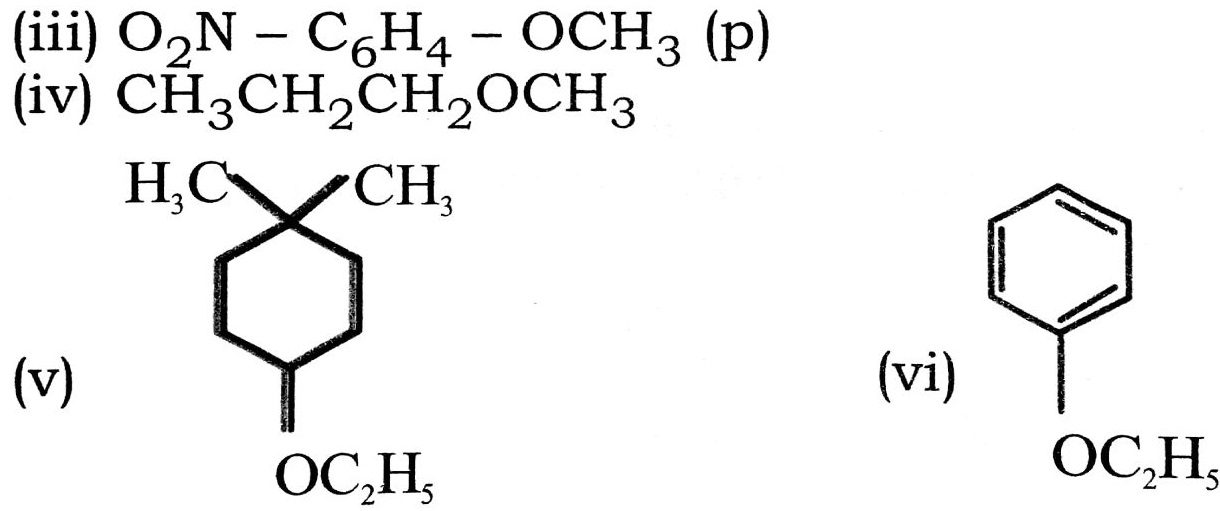
Ans⇒ (i) 1-Ethoxy-2-methyl propane.
(ii) 2-Chloro-1-methoxy ethane.
(iii) 4-Nitro anisole.
(iv) 1-Methoxy propane.
(v) 1-Ethoxy-3-methyl cyclo hexane.
(vi) Ethoxy benzene.
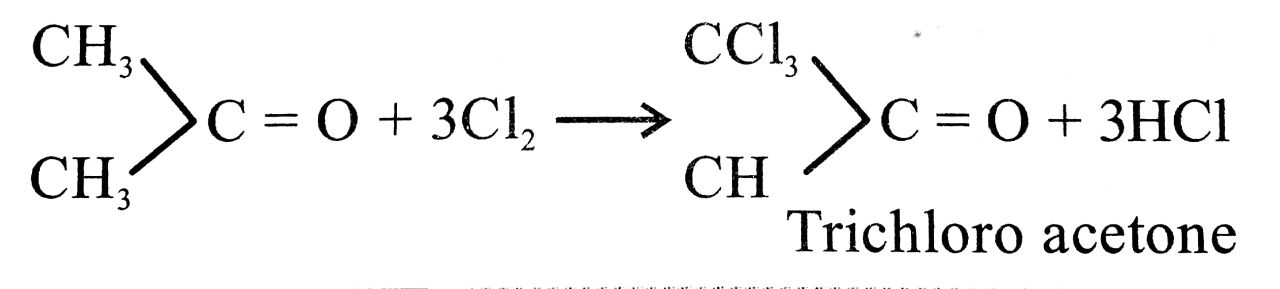
Q. 9. How is chloroform obtained from acetone ?
Ans⇒ Acetone on warming with moist bleaching powder chloroform is obtained on distillation. The series of reactions are
Ca(OCl) Cl + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + Cl2
![]()
Q. 10. Give two methods of preparation of ethers from alcohol with chemical equations.
Ans⇒ Following methods of preparation of ethers from alcohol :
(i) From the reaction between alcohol and conc. H2SO4
ROH + ROH![]() R-O-R + H2O
R-O-R + H2O
(ii) From dehydration of alcohol :
R- OH + R – OH ![]() R-O-R+H2 O
R-O-R+H2 O
