
10. HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES – LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
10. HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
Q. 1. Give the uses of Freon 12, DDT, carbon tetrachloride and iodoform.
Ans⇒ (i) Freon-12 :
Preparation : The chlorofluorocarbon compounds of methane and ethane are collectively known as freons. Dichloro difluoro methane (Freon 12) is the most common freons. It is manufactured from tetrachloro methane by the action of antimony trifluoride in the presence of antimony pentafluoride. This is known as swarts reaction.
3CCl4 + 2SbF3 + 3CCl2F2 +2SbCl3
Carbon Antimony (Freon)
tetrachloride trifluoride.
Uses : (a) It is used as a refrigerant (cooling agent) in refrigerators and air conditioners.
(b) It is also used as a propellant in aerosols and foams to spray out deodorants, cleaners, hair sprays, shaving creams.
(c) It is also used as insecticides.
(ii) DDT (p, p’-Dichlorodiphenyl trichloro ethane) :
Preparation : It is manufactured by the conden sation of chlorobenzene with trichloro acetal-dehyde (chloral) in the presence of sulphuric acid.
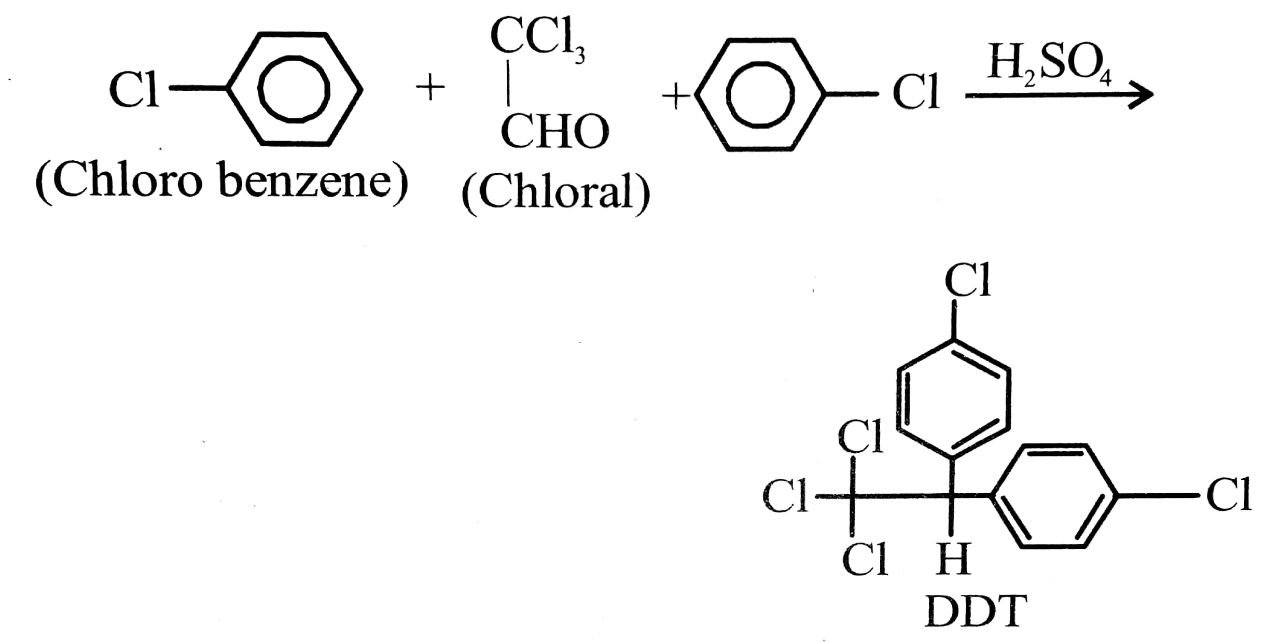
uses: (a) It is powerful insecticide. It is highly stable and not easily decomposed.
(b) It is used for killing insects and mosquitoes.
(iii) Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) :
PreParation : It is prepared industrially by chlorination of methane and by the action of chlorine
on carbon disulphide in the presence of aluminium chloride as catalyst.
(i) CH4 + 4Cl2 ![]() CCl4 + 4HCl
CCl4 + 4HCl
(ii) CS2 + 3Cl2 ![]() CCl4 + S2Cl2
CCl4 + S2Cl2
Carbon Carbon Sulphur
disulphide tetrachloride monochloride
Uses : (a) It is used as a solvent for oils, fats and waxes.
(b) It is used as a fire extinguisher under the name pyrene.
(c) It is used as dry cleaning.
(d) It is used for the manufacture of freon.
(iv) Iodoform (CHI3) :
Preparation : It is prepard by using ethanol or acetone with sodium hydroxide and iodine or sodium carbonate and iodine in water.
(a) CH3CH2OH + 6NaOH + 4l2 ![]()
. CHI3 + HCOONa + 5H2O + 5NaI (Iodoform)
(b) CH3COCH3 + 4NaOH + 3I2 ![]()
. CHI3CH3COONa + 3H2O + 3NaI (Iodoform)
Uses : (a) It is used as an antiseptic and this nature is due to iodine that it liberates. However, because of its very unpleasant smell, it has now been replaced by better antiseptics.
(b) It is used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals.
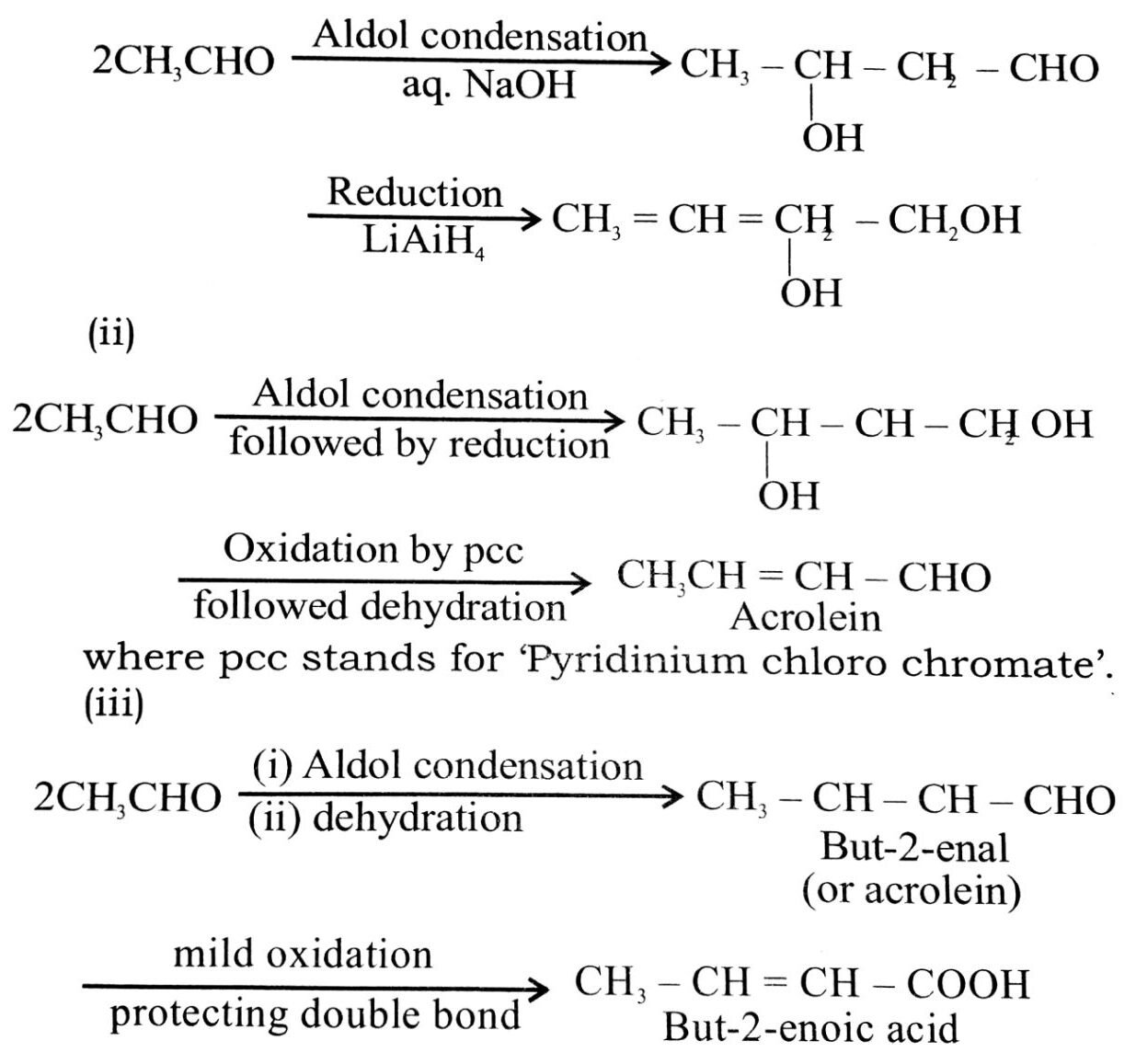
Q. 2. How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds ?
(i) Butane-1,3-diol
(ii) But-2-enal
(iii) But-2-enoic acid.
Ans⇒ (i)
Q. 3. Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions :


Q. 4. Draw the structure of all eight strutural isomers that have the molecular formula C5H11Br. Name each isomer according to IUPAC system and classify them as primary, secondary or tertiary bromide.
Ans⇒ CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2Br……..1-Bromopentane (1°)
CH2CH2CH2CHBr CH3……………..2 -Bromopentane (2°)
CH3CH2CH (Br) CH2CH2…. ………3 -Bromopentane (2°)
(CH3)2 CHCH2CH2Br…..1-Bromo-3-methyl butane (1°)
(CH3)2 CHCHBrCH3…….2-Bromo-3-methyl butane (2°)
(CH3)2 CBrCH2CH3……..2-Bromo-2-methyl butane (3°)
CH3 CH2 CH(CH)3 CH2Br …1-Bromo-2-methyl butane (1°)
(CH3)3 CCH2Brl……..-Bromo-2, 2-dimethyl propane (1°)
Q. 5. Write the chemical equations for the following conversions :
(i) Chloroform to acetic acid.
(ii) Acetaldehyde to chloroform.
(iii) Chloroform to ethyne (acetylene).
(iv) Ethanol to chloroform.

Q. 6. Write the structure of isomers of C5H11Br.
Ans. (i) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2Br
1-bromopetane

2,2-dimethyl-1-bromo pentane
Q. 7. Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions :
(a) CH2CH2CH2Cl + NaI![]()
(b) (CH3)3CBr + KOH ![]()
(c) CH2CH(Br)CH2CH3 + NaOH ![]() aq. ethanol
aq. ethanol
(d) CH3CH2Br + KCN →
(e) C6H5ONa + C2H5Cl →
(f) CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 →
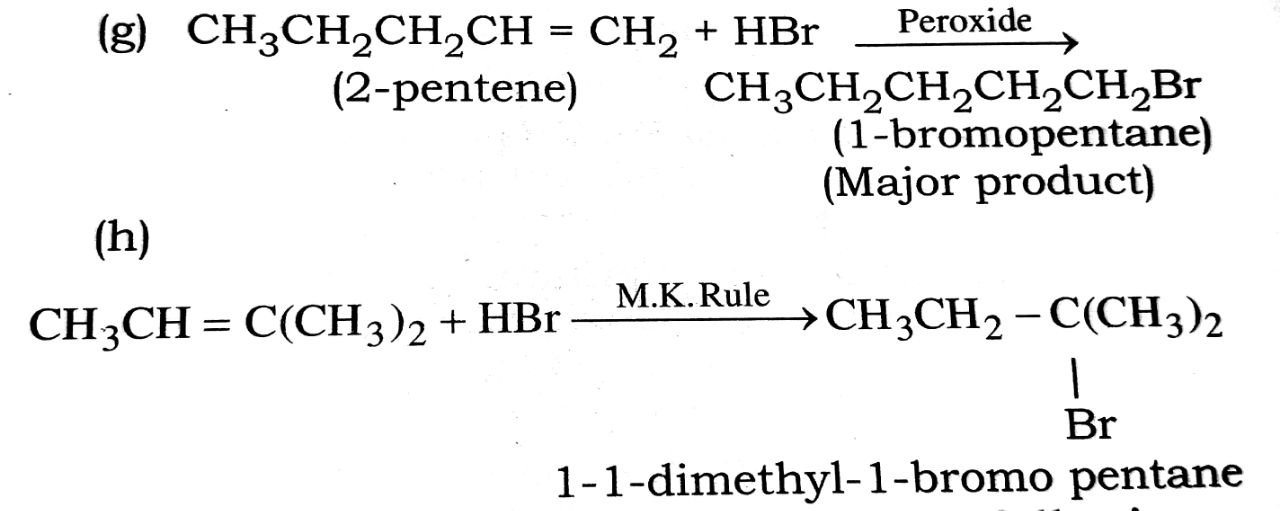
(g) CH3CH2CH = CH + HBr ![]()
(h) CH3CH = C(CH3)2 + HBr →
Ans⇒ (a)
CH3CH2CH2Cl + Nal ![]() CH3CH2CH2I + NACl
CH3CH2CH2I + NACl
(Propyl chloride) (Major product)
(b) (CH3)3CBr + KOH → ![]() – C = CH2 + KBr
– C = CH2 + KBr
Tertiary butyl bromide Isobutane
. (Major product)
(c) CH3CH(Br) CH2CH3 + NaOH ![]()
(2- bromo butane)
CK3CH = CHCH3 + CH3CH2OH = CH2
(but-2 -ene) (but-1 -ene)
(Major product) (Minor product)
(d) CH3 CH2Br + KCN ![]() CH3CH2C ≅ KBr
CH3CH2C ≅ KBr
(e) C6H5ONA + C2H5Cl ![]() C6H5OC2H5 + NaCl
C6H5OC2H5 + NaCl
. (Ethoxy benzyl ethane)
(f) CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 → CH3CH2CH2Cl + SO2 + HCl
(Propan- l -ol) Propyl chloride
. (Major product)
. Peroxide
Q. 8. Give the IUPAC name of the following:
(a) (CH3)2 CHCH2I
(b) (CH3)2CHCICH3
(c) CH3CHBr (CH3)2 CH2CH
(d) (CH3)2 CClCBr(CH3)2.

2-chloro-2- methyl propane
(c) CH3CHBrC (CH)3)2 CH2CH3
4-Bromo, 3- dimethyl pentane
(d) (CH3)2CClCBr(CH3)2
1-Bromo dimethyl 2- chloro 2 methyl propane
Q. 9. Explain why is ortho-nitrophenol more acidic than rthomethoxy benzene ?
Ans⇒ 
NO2 group is electron withdrawing due to resonace and inductive effect will OCH3 group has + R effect and increases the electron density arounds H of O–H group. There fore, removal of Has H+ ion is easier in o-nitrohenol than in o-methoxy benzene. Hence, o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxy benzene.


