8. ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES ( SHORT QUESTION ANSWER 2022 )
8. ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
Q. 1. State the principle of production of em waves.
Ans ⇒The accelerated charge produces electric and magnetic fields, which vary both in space and time. These varying electric and magnetic fields give use to electromagnetic waves.
Q. 2. State two application of radio waves, micro waves, γ-rays, IR-rays, UV-rays and X-rays.
Ans ⇒ Two application of radio waves :
(i) Radio waves are used in radio astronomy.
(ii) Radio waves are used for wireless communication purposes.
Two application of micro waves :
(i) Micro waves are used in the study of atomic and molecular structure.
(ii) Micro waves are used in radar systems and in long distance telephone communication systems.
Two application of γ-rays :
(i) γ-rays are used in radiotherapy to treat tumours and cancer.
(ii) γ-rays (soft γ-rays) are used to kill micro organisms in food industry so as to preserve food stuffs for a longer time,
Two application of IR-rays :
(i) IR-rays are used to treat muscular strains.
(ii) IR-rays are used to provide electrical ener to satellites by using solar cells.
Two application of UV-rays :
(i) UV-rays are used to check the mineral samples by making use of its property of causing flourescence.
(ii) UV-rays are used in burglar alarmns as they can cause photoelectric effect.
Two application of X-rays :
(i) X-rays are used in surgery for detection of fractures, diseased organs etc.
(ii) X-rays are used in radio therapy.
Q.3. Write three properties of infra-red rays. UV-rays and X-rays.
Ans ⇒ Three properties of infra-red rays :
(i) They are e.m. waves and travel with the speed of light in vacuum.
(ii) They obey laws of reflection and refraction.
(iii) They affect a photographic plate.
Three properties of UV-rays rays :
(i) They obey the laws of reflection and refraction.
(ii) They can undergo interference and can be polarised.
(iii) They can cause flourescence in certain materials.
Three properties of X-rays :
(i) They can undergo reflection, refraction, interference diffraction and polarisation.
(ii) They affect photographic plates.
(iii) They cast shadows of the objects falling in their path due to the reason that they travel in a straight line.
Q.4. How you can establish that light waves are transverse in nature ?
Ans ⇒ A polariser P and analyser A be placed in such a way that their crystallographic axes are parallel to each other as shown in figure. When ordinary light is allowed to fall on crystal P, it is seen that intensity of light finally transmitted by analyser A is nearly half of the original value of the intensity of light incident on polariser P. If the analyser A is now rotated then the intensity of transmitted light through A goes on decreasing. When the axes of two crystal become perpendicular, the intensity of light emerging from A becomes minimum. This obervation clearly verifies that vibrations in light emerging from A becomes minimum. This obervation clearly verifies that vibrations in light waves are transverse.

Q.5. Find an expression for the velocity of electro-magnetic waves.
Ans ⇒ Changing electric field is the source of changing magnetic field and changing magnetic field is the source of changing electric field.

Q.6. Establish a relation between displacement current and conduction current.
Ans ⇒ The displacement current.
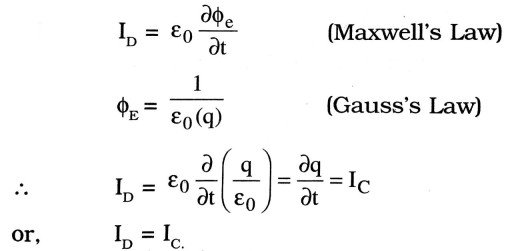
Q.7. What is sky wave propagation of waves ? Explain why sky wave transmission of electromagnetic waves cannot be used for TV transmission.
Ans ⇒ In sky wave propagation, transmitted wave goes up in the sky and is reflected back from the ionosphere. Waves transmitted towards ionosphere suffer total internal reflection. Frequency of the wave reflected depends upon electron density (N) of particular layer of ionosphere. For a given value of N there is a critical frequency above which wave does not suffer T.I.R.
Fe = 9(Nmax)1/2
There is a range of critical frequencies approximately from 5 to 10 MHz. Frequencies higher than this cross the ionosphere and do not return back to the earth.
As TV transmission takes place at frequencies higher than 10 MHz (= 80 MHz to 200 MHz) sky wave transmission of electromagnetic waves cannot be used.
Q.8. What is displacement current ? Explain its cause.
Ans ⇒ Displacement current is that current which is produced in a region, where ever the electric field and hence the electric slux is changing with time. The displacement current is given by
![]()
alt Where ε0 = absolute permitivity of space
![]() rate of change of electric flux.
rate of change of electric flux.
Q.9. State the five properties of electromagnetic waves.
Ans ⇒ The following are the properties of electromagnetic waves :
(i) They are transverse in nature.
(ii) They travel with the same speed of light in vacuum (i.e., C = 3 x 108 ms-1) and in a material medium their velocity is u and t are absolute permeability and permitivity of that medium.
(iii) They don’t require any material medium for their propagation.
(iv) They consist of mutually transverse varying electric and magnetic field.
(v) They are produced by accelerated or oscillating charge.
Class 12th physics Subjective question in English
| S.N | Physics Short Type Question English Medium |
| 1. | ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS |
| 2. | LECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE |
| 3. | CURRENT ELECTRICITY |
| 4. | MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM |
| 5. | MAGNETISM AND MATTER |
| 6. | ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION |
| 7. | ALTERNATING CURRENT |
| 8. | ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES |
| 9. | RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS |
| 10. | WAVE OPTICS |
| 11. | DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION |
| 12. | ATOMS |
| 13. | NUCLEI |
| 14. | SEMI CONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS |
| 15. | COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS |
