
15. POLYMERS Objective
15. POLYMERS
1. Bakelite is an example of –
(A) elastomer
(B) fibre
(c) thermoplastic
(D) thermosetting
2. Arrange the following polymers is an increasin order of intermolecular forces; fibre, plastic, elastomer-
(A) Elastomer < Fibre < plastic
(B) Elastomer < Plastic < Fibre
(C) Plastic < Elastomer < Fibre
(D) Fibre < Elastomer < Plastic
3. The correct structure of monomers of buna-S is
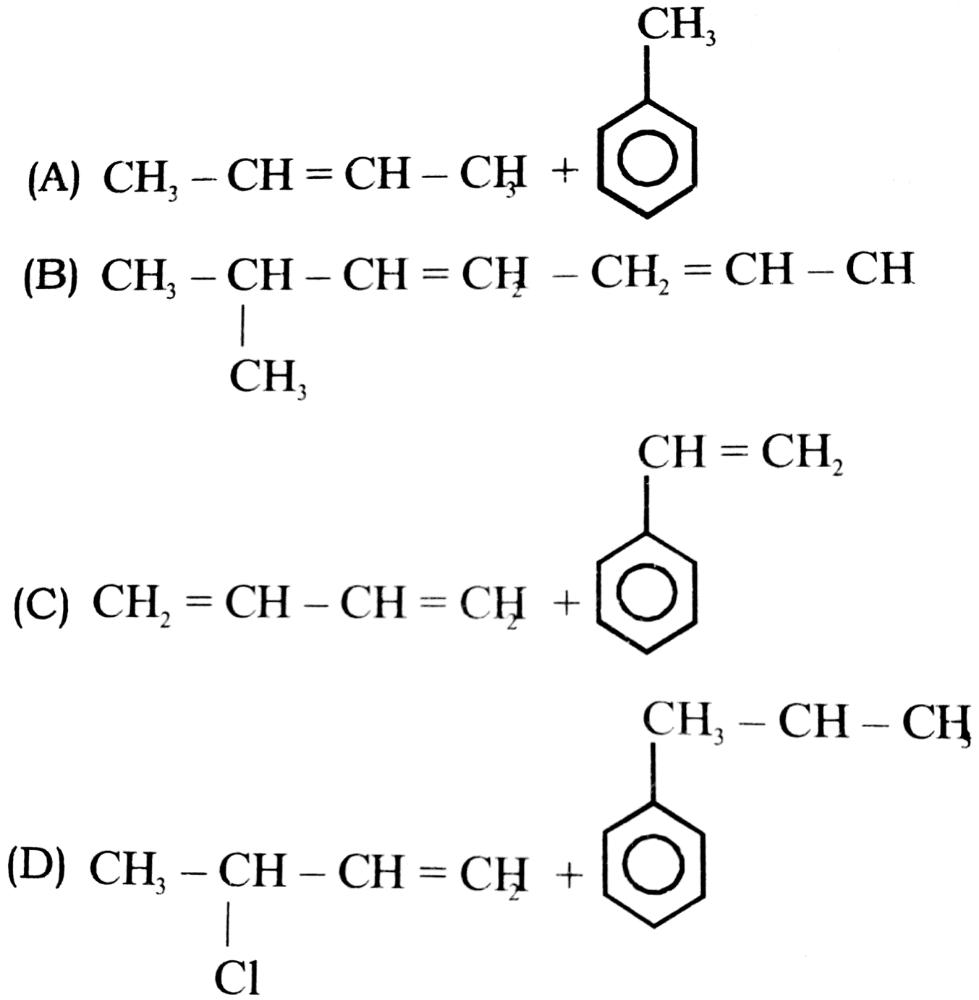
Ans. (C)
4. The S in buna-S refers to
(A) Sulphur
(B) Styrene
(C) Sodium
(D) Salicylate
5. Identify the type of polymer
(i) – A – A – A – A – A – A –
(ii) – A – B – B – A – A – A – B – A –
(A) (i) Homopolymer, (ii) Copolymer
(B) (i) Natural polymer, (ii) Synthetic polymer
(C) (i) Linear polymer, (ii) Branched polymer
(D) (i) Fibre, (ii) Elastomer
6. Which of the following are thermoplastic polymers ?
(A) Polythene, urea-formaldehyde, polyvinyls
(B) Bakelite, polythene, polystyrene
(C) Polythene, polystyrene, polyvinyls
(D) Urea-formaldehyde, polystyrene, bakelite
7. Nylon 6, 6 is obtained by condensation polymerisation of
(A) adipic acid and ethylene glycol
(B) adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine
(C) terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol
(D) adipic acid and phenol
8. Natural rubber is a polymer of
(A) 1, 1-dimethylbutadiene
(B) 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene
(C) 2-chlorobuta-1, 3-diene
(D) 2-chlorobut-2-ene
9. Dacron is an example of
(A) polyamides
(B) polypropenes
(C) polyacrylnitrile
(D) polyesters
10. Composition of Ziegler-Natta catalyst is
(A) (Et3)3Al.Ticl2
(B) (Me)3Al.TiCl2
(C) (Et)3Al.TiCl4
(D) (Et)3Al.PtCl4
11. Which of the following is a homopolymer ?
(A) Bakelite
(B) Nylon 6,6
(C) Neoprene
(D) Buna-S
12. Polymer which has amide linkage is
(A) nylon-6, 6
(B) terylene
(C) teflon
(D) bakelite
13. In vuclanization of rubber
(A) sulphur reacts to form a new compound
(B) sulphur cross-links are introduced
(C) sulphur forms a very thin protective layer over rubber
(D) All statements are correct
14. Novolac on heating with formaldehyde undergoes ……… to form an infusible solid mass called ………
(A) polymerisation, melamine
(B) vulcanisation, resin
(C) cross-linking, bakelite
(D) condensation, polystyrene
15. Synthetic biopolymer, PHBV is made up of the following monomers
(A) 3-hydroxybutanoic acid + 3-hydroxypentanoic acid
(B) 2-hydroxybutanoic acid + 2-hydroxypentanoic acid
(C) 3-chlorobutanoic acid + 3-chloropentanoic acid
(D) 2-chlorobutanoic acid + 3-methylpentanoic acid
16. Which of the following is a biodegradable synthetic polymer ?
(A) Aliphatic polyesters
(B) PHBV
(C) Nylon-2-nylon-6
(D) All of these
17. Which of the following polymers of glycose is stored by animals ?
(A) Cellulose
(B) Amylose
(C) Amylopectin
(D) Glycogen
18. The commercial name of polyacrylonitrile is
(A) dacron
(B) orlon (acrilan)
(C) PVC
(D) bakelite
19. Which of the following polymers are used as fibre ?
(A) Nylon
(B) Polytetrafluoroethane
(C) Terylene
(D) Buna-S
20. Sweetest of all sugars is
(A) Glucose
(B) Lactose
(C) Sucrose
(D) Fructose
21. Glucose is
(A) Triose
(B) Tetrose
(C) Fentose
(D) Hexose
22. Which vitamin deficiency causes night blindness ?
(A) Vitamin A
(B) Vitamin B
(C) Vitamin C
(D) Vitamin D


