
13.AMINES Objective
14.AMINES
1. Nitrogen atom of amino group is ……….. hybridised.
(A) sp
(B) sp2
(C) sp3
(D) sp3d
2. The most convenient method to prepare primary (i Amine) amine containing one carbon atom less is
(A) Gabriel phthalmidie synthesis
(B) Reductive amination of aldehydes
(c) Hofmann bromamide reaction
(D) Reduction of isonitriles
3. When excess of ethyl iodide is treated with ammonia, the product is
(A) ethylamine
(B) diethylamine
(C) triethylamine
(D) tetrathylammonium iodide
4. Secondary amines can be prepared by
(A) reduction of nitro compounds
(B) oxidation of N-substituted amides
(C) reduction of isonitriles
(D) reduction of nitriles
5. Amine that cannot be prepared by Gabriel- Phthalmidie synthesis is
(A) aniline
(B) benzyl amine
(C) methyl amine
(D) iso-butylamine
6. Which of the following amines will give carbylamine reaction ?
(A) (C2H5)3N
(B) (C2H5)2NH
(C) C2H5NH2
(D) C3H7NHC2H5
7. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of basicity :
CH3NH2, (CH3)2 NH, NH3, C6H5NH2
(A) C6H5NH2 < NH3 < (CH3)2NH < CH3NH2
(B) CH3NH2 < (CH3)2NH < NH3 < C6H5NH2
(C) C6H5NH2 < NH3 < CH3NH2 < (CH3)2NH
(D) (CH3)2NH < CH3NH2 < NH3 < C6H5NH2
8. Which of the following species are involved in the carbylamine test ?
(i) RNC
(ii) CHCl3
(iii) COCl2
(iv) NaNO2 + HCl
(A) (i) and (iv)
(B) (i) and (ii)
(C) (ii) and (iv)
(D) (ii) and (iii)
9. Identify ‘Z’ in the sequence ?
C6H5NH2 ![]()
(A) C6H5CN
(B) C6H5CONH2
(C) C6H5COOH
(D) C6H5CH2NH2
10. Which of the following is used as Hinsberg’s reagent ?
(A) C6H5SO2Cl
(B) C6H5SO3H
(C) C6H5NHCH3
(D) C6H5COCH3
11. Among the compounds C3H7NH2, CH3NH2, C2H5NH2 and C6H5NH2. Which is the least basic compound ?
(A) CH3NH2
(B) C2H5NH2
(C) C3H7NH2
(D) C6H5NH2
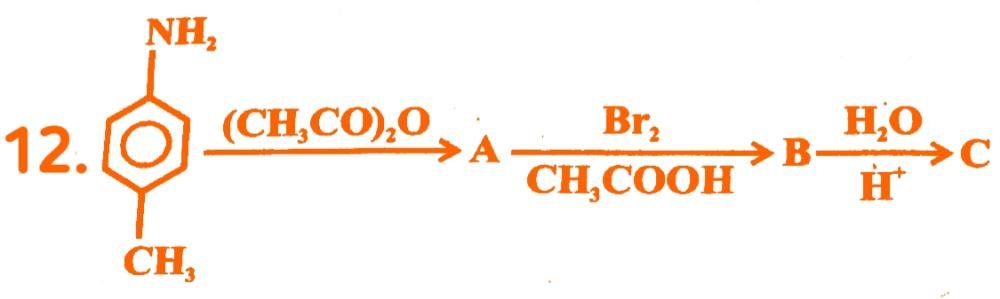
Product would be

13. Most basic species amongst the following is

14. When aniline is heated with conc. H2SO4 at 455-475 K, it forms
(A) aniline hydrogensulphate
(B) sulphanilic acid
(C) amino benzene sulphonic acid
(D) benzenesulphonic acid
15. Which of the following compounds reacts with NaNO2 and HCl at 0-4°C to give alcohol/ phenol ?
(A) C6H5NH2
(B) C2H5NH2
(C) CH3NHCH3
(D) C6H5NHCH3
16. Which of the following has highest pKb value ?
(A) (CH3)3CNH2
(B) NH3
(C) (CH3)2NH
(D) CH3NH2
17. Acetylation of a secondary amine in alkaline medium yields
(A) N, N-dialkyl acetainide
(B) N, N-dialkyl amine
(C) N, N-dialkyl amide
(D) acetyl dialkyl amine
18. When p-toluidine reacts with chloroform and alcoholic KOH, then the product is
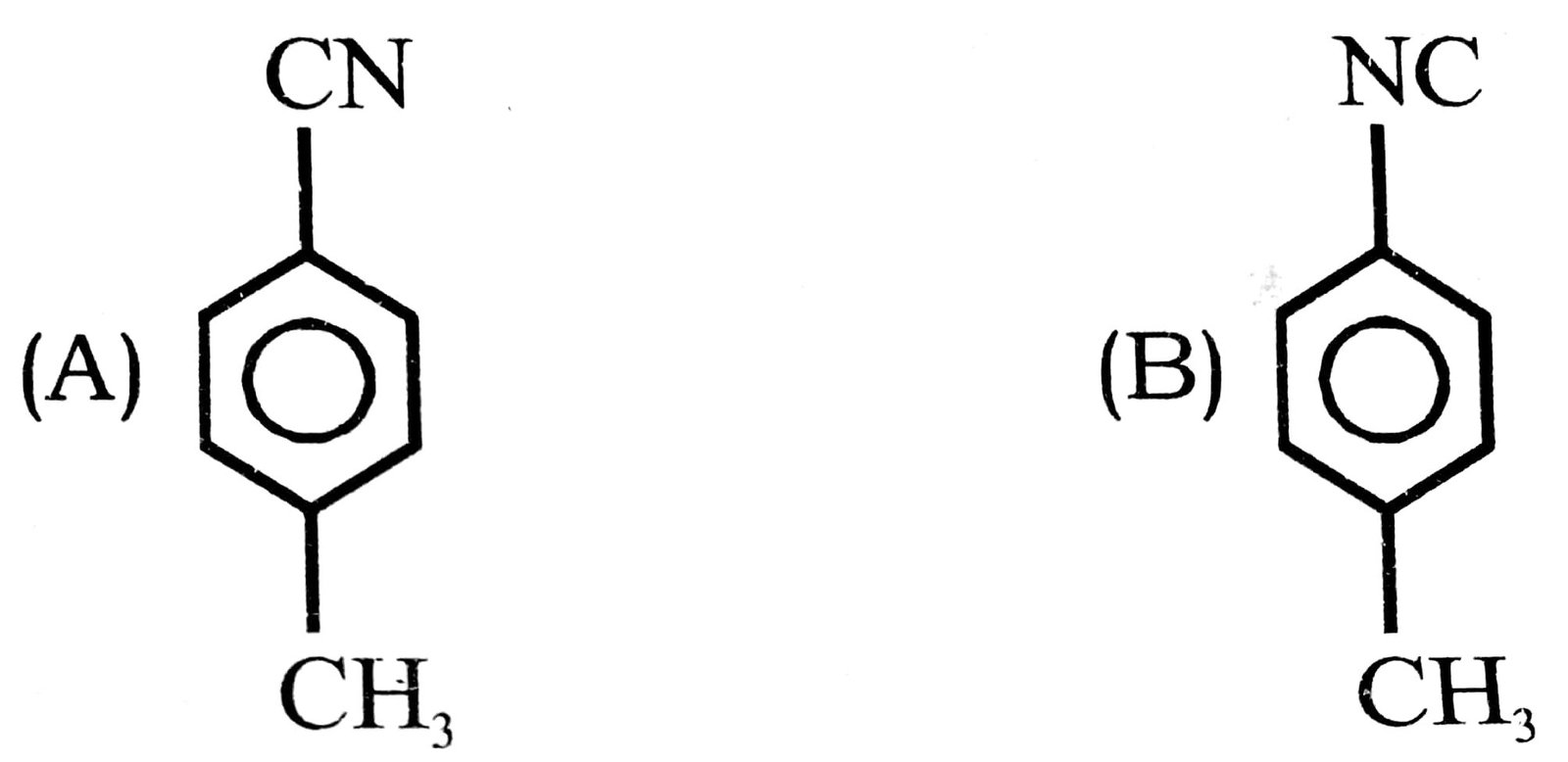

19. Among the following:
I. CH3NH2
II. (CH3)2NH
III. (CH3)3N
IV. C6H5NH2
Which will give the positive carbylamine test ?
(A) I and II
(B) I and IV
(C) II and IV
(D) II and III
20. Cyclohexylamine is stronger base than aniline become
(A) in aniline electron pair is involved in conjugation
(B) in cyclohexylamine electron pair is involve conjugation
(C) in aniline-NH2 group is protonated
(D) in cyclohexylamine nitrogen has a negative charge
21. The strongest base among the following is
(A) C6H5NH2
(B) p-NH2C6H4NH
(C) m-NO2C6H4NH2
(D) C6H5CH2NH2
22. Among the following the weakest base is
(A) CH3NHCHO
(B) C6H5CH2NH2
(C) NO2CH2NH2
(D) C6H5CH2NHCH3
23. o-Chloroaniline is treated with a mixture of NaNO2 and HCl and the product is reacted with cuprous bromide. The final product in the reaction will be

24. In diazotisation reaction with NaNO2 and HCI an excess of HCl is used to
(A) suppress the formation of acetanilide
(B) suppress the concentration of free aniline available for coupling
(C) maintain the pH of the reaction
(D) prevent the formation of anilinium ion
25. The correct IUPAC name for CH2 = CHCH2NHCH3 is
(A) allylmethylamine
(B) 2-amino-4-pentene
(C) 4-aminopent-1-ene
(D) N-methylprop-2-ene-1-amine
26. Benzylamine may be alkylated as shown in the following equation :
C6H5CH2NH2 + R – x → C6H5CH2NHR + HX
Which of the following alkyl halides is best suited for this reaction through SN1 mecha-nism ?
(A) CH3Br
(B) C6H5Br
(C) C6H5CH2Br
(D) C2H5Br
27. Which of the following reagents would not be a good choice for reducing an aryl nitro compound to an amine ?
(A) H2 (excess)/Pt
(B) LiAlH4 in ether
(C) Fe and HCl
(D) Sn and HCl
28. In order to prepare a 1° amine from an alkyl halide with simultaneous addition of one CH2 group in the carbon chain, the reagent used as source of nitrogen is
(A) sodium amide, NaNH2
(B) sodium azide, NaN3
(C) potassium cyanide, KCN
(D) potassium phthalimide, C6H4(CO)2N–K+
29. Amongst the given set of reactants, the most approp. for preparing 2° amine is
(A) 2° R – Br + NH3
(B) 2° R – Br + NaCN followed by H2/Pt
(C) 1°R – NH2 + RCHO followed by H2/Pt
(D) 1° R – Br (2 mol) + potassium phthalimide followed by H3O+ / heat
30. The correct increasing order of basic strength for following compounds is

(A) II < III <I
(B) III < I< II
(C) III < II <I
(D) II < I < III
31. The gas evolved when methylamine reacts with nitrous acid is
(A) NH3
(B) N2
(C) H2
(D) C2H6
32. Best method for preparing primary amines from alkyl halides without changing the number of carbon atoms in the chain is
(A) Hofmann bromamide reaction
(B) Gabriel phthalmide synthesis
(C) Sandmeyer reaction
(D) Reaction NH3
33. Which of the following compounds will not undergo azo coupling reaction with benzene dianonium chloride ?
(A) Aniline
(B) Phenol
(C) Anisole
(D) Nitrobenzene
34. Aniline reacts with Acetaldehyde to form
(A) Carbylamines
(B) Nitrogenzene
(C) Imine
(D) Schifs base
35. Imprical formulae of benzene is
(A) CH
(B) C2H2
(C) C6H6
(D) None


